Seismisitas, Energi dan Percepatan Tanah Dalam Penentuan Tingkat Resiko Gempabumi Di Wilayah Sulawesi Tengah
Abstract
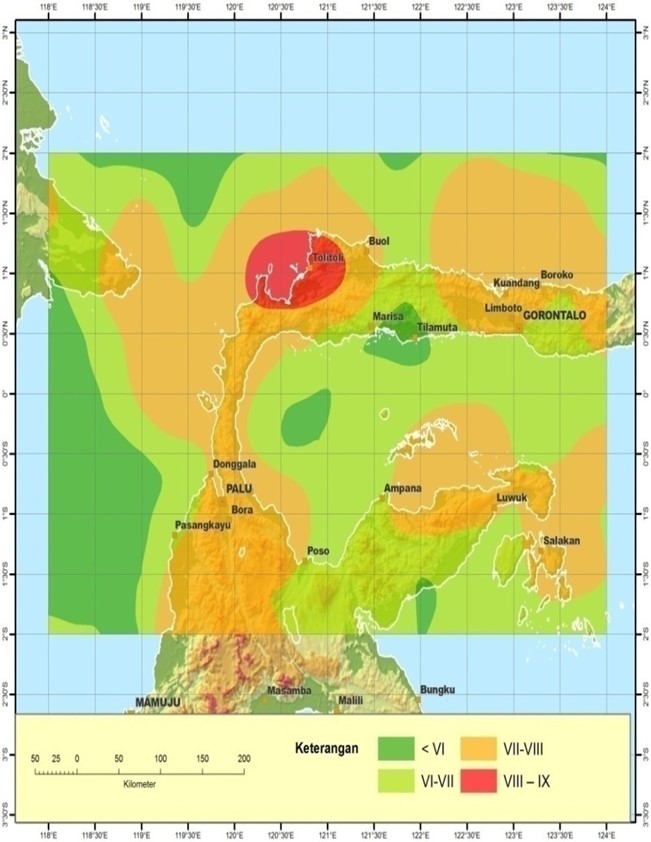
Sejarah gempabumi di wilayah Sulawesi Tengah sudah beberapa kali mencatatkan gempa besar, sebagian diantaranya menimbulkan tsunami sehingga menyebabkan berbagai kerusakan bahkan menyebabkan kematian. Hasil dari sebaran episenter memberikan gambaran mengenai tingkat seismisitas di wilayah Sulawesi Tengah, terlihat bahwa tingkat kegempaan di wilayah ini sangat kompleks. Frekuensi banyaknya kejadian gempa didominasi oleh gempa-gempa dangkal dengan kedalaman kurang dari 70 km. Hasil perhitungan energi total gempa tertinggi terletak di wilayah Luwuk sebesar 7,9572121 erg. Nilai percepatan tanah maksimum paling besar diperoleh di daerah Tolitoli tepatnya pada koordinat 1,02o LU dan 120,40o BT yaitu sebesar 215,6651 gal. Penentuan wilayah resiko gempa didasarkan pada klasifikasi nilai hasil perhitungan percepatan tanah maksimum dan intensitas maksimum menjadi kategori resiko sangat kecil hingga resiko besar. Hampir seluruh wilayah Sulawesi Tengah memiliki resiko bencana gempabumi yang cukup tinggi di mana daerah Tolitoli memiliki tingkat resiko paling tinggi dengan nilai percepatan tanah 215,6651 gal dan nilai intensitas maksimum VIII-IX MMI.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Hall, R., & Wilson, M. E. J. Neogene sutures in eastern Indonesia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(6), 781-808. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00040-7, 2000.
Katili, J. A. A review of the geotectonic theories and tectonic maps of Indonesia. Earth-Science Reviews, 7(3), 143-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(71)90006-7, 1971.
Katili, J. A. Review of past and present geotectonic concepts of eastern indonesia. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 24(2-3), 103-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0077-7579(89)90143-9, 1989.
Pakpahan, S., Ngadmanto, D., Rohadi, S., Widodo, H. S., Susilanto, P., Bmkg, P., & Angkasa, J., Analisis Kegempaan di Zona Sesar Palu Koro, Sulawesi Tengah. Jurnal Lingkungan dan Bencana Geologi, 6(3), 253-264, 2015.
Bock, Y., Prawirodirdjo, L., Genrich, J. F., Stevens, C. W., McCaffrey, R., Subarya, C., Puntodewo, S. S. O., & Calais, E., Crustal motion in Indonesia from Global Positioning System measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B8). https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000324, 2003.
Jayadi, H., Analisis Seismotektonik Untuk Penanggulangan Daerah Rawan Bencana Gempa Bumi. Jurnal Fisika dan Terapannya, 3, 110-116, 2016.
Kasahara, K. Earthquake Mechanics Meterology and Geophysics. New York: University Press Cambridge, 1969.
Bellier, O., Sebrier, M., Beaudouin, T., Villeneuve, M., Braucher, R., Bourles, D., Siame, L., Putranto, E., & Pratomo, I., High slip rate for a low seismicity along the Palu-Koro active fault in central Sulawesi (Indonesia). Terra Nova, 13(6), 463-470. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3121.2001.00382.x, 2001.
Daryono. Tataan Tektonik Dan Sejarah Kegempaan Palu, Sulawesi Tengah. 3, 2011.
Garini, S. A., & Rahmawati, E., Relokasi Hiposenter Gempa Bumi di Sulawesi Tengah Dengan Menggunakan Metode Geiger Dan Coupled Velocity-Hypocenter. Jurnal Fisika, Unversitas Negeri Surabaya, 3(2), 107-112, 2014.
Juwitarini, A., Analisis Model Kecepatan Tomografi 3d Body Waves Pada Gempa Bumi Di Wilayah Sulawesi Tengah Tahun 2008-2018 Menggunakan Lotos-12. 7, 2019.
Ismullah M., Muh. F., Lantu, Aswad, S., & Massinai, Muh. A., Tectonics earthquake distribution pattern analysis based focal mechanisms (Case study Sulawesi Island, 1993-2012). 030013. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4915021, 2015.
Muhammad Fawzy Ismullah, M., Dian Nugraha, A., Ramdhan, M., & Wandono., Precise Hypocenter Determination around Palu Koro Fault: A Preliminary Results. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 62, 012056. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/62/1/012056, 2017.
Supendi, P., Nugraha, A. D., & Widiyantoro, S. Hypocenter relocation of the aftershocks of the Poso, Sulawesi (Mw 6.6, May 29, 2017) event using the BMKG network data. 020076. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5047361, 2018.
Supendi, P., Nugraha, A. D., Widiyantoro, S., Pesicek, J. D., Thurber, C. H., Abdullah, C. I., Daryono, D., Wiyono, S. H., Shiddiqi, H. A., & Rosalia, S. Relocated aftershocks and background seismicity in eastern Indonesia shed light on the 2018 Lombok and Palu earthquake sequences. Geophysical Journal International, 221(3), 1845-1855. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggaa118, 2020
Jayadi, H., Mukaddas, A., & Meidji, I. U., Investigasi Bidang Gelincir Pada Daerah Rawan Longsor Di Ruas Jalan Tawaeli-Toboli Menggunakan Metode Geolistrik Tahanan Jenis. Jurnal Fisika Unand, 9(3), 381-387. https://doi.org/10.25077/jfu.9.3.381-387, 2020.
Soehaimi, A., Mikrotremor Dan Percepatan Tanah Maksimum Kota Makassar. Jurnal Geologi dan Sumberdaya Mineral, 19(1), 37-45. https://doi.org/10.33332/jgsm.geologi.v19i1.192, 2009
Sunarjo, G., & Pribadi, S., Gempa Bumi Edisi Populer. BMKG, Jakarta, 2010.
Kapojos, C. G., Tamuntuan, G., & Pasau, G., Analisis Percepatan Tanah Maksimum Dengan Menggunakan Rumusan Esteva Dan Donovan (Studi Kasus Pada Semenanjung Utara Pulau Sulawesi). JURNAL ILMIAH SAINS, 15(2), 99-104. https://doi.org/10.35799/jis.15.2.2015.9225, 2015.
Linkimer, L., Relationship Between Peak Ground Acceleration and Modified Mercalli Intensity in Costa Rica. Revista Geológica de América Central, 38. https://doi.org/10.15517/rgac.v0i38.4218, 2007.
Fukushima, Y., & Tanaka, T., A new attenuation relation for peak horizontal acceleration of strong earthquake ground motion in Japan. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 80(4), 757-783, 1990.
Gutenberg, B., The energy of earthquakes. Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society, 112(1-4), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.JGS.1956.112.01-04.02, 1956.
Bath, M. Introduction to Seismology. Birkhäuser, 2013.
Supartoyo, Sulaiman, C., & Junaedi, D., Kelas tektonik sesar Palu Koro, Sulawesi Tengah. Jurnal Lingkungan dan Bencana Geologi, 5(2), 111-128, 2014.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.34312/ljpa.v1i1.18558
Copyright (c) 2022

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


